Handy Git commands

Version control is now being implemented by almost all the organizations which would be very very important for collaboration, tracking and etc..
Version controlling/management is followed by QA team as well. I have been using the free version management system GIT on different projects. So I wanted to list out the most used and handy git commands.
How to make your local folder as a git repository
Prerequisites :- Install git in your computer
- Go to github.com and create a repository. Copy the repository url, which is something like this. ex: https://github.com/username/repoName.git
- Keep the github login credentials handy. Git prompts you for credentials while pushing the code
In command prompt go to the folder which you want to link up with a remote git repository. And type
git init
Connect to your remote repository usinggit remote add origin https://github.com/username/repoName.git
Add the files/folders you want to push to remote repo usinggit add /folder/filename.extension
orgit add /folder/*.extension
Then commit your added files with a commit messagegit commit -m 'Initial commit'
Now push the code to remote usinggit push -u origin branchName
example : git push -u origin master
Hurray..!! Great Job, Now if you go to your github repository you can see all the code you have just pushed.How to Clone the existing repository
In general we will not push the code directly to master branch, because master branch is the branch which will be used as a base for all the team. If we push the code with errors directly to master branch it will affect the entire team. So first we need to push the code to a secondary branch, if everything is okay then we will merge that to master branch. So we create a separate branch for our work and if every thing is okay on that branch, then we will merge that branch to the master/intended branch. usually a 3 level structure is followed.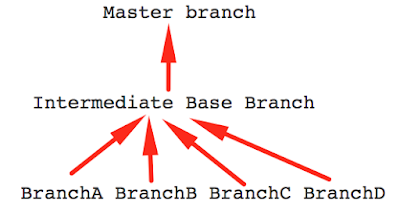
So every individual work goes to the intermediate base branch, if everything is okay from that branch then that branch will be merged to the master branch.
To clone the existing remote repository
To get the latest changes from remote to local
checkout to the branch in local and then
git clone username@https://github.com/username/repoName.git:/path/to/repository
To get the latest changes from remote to local
git pull origin/branchName
Another way :checkout to the branch in local and then
git fetch --al
git rebase origin/branchName
How to manage local branches
Creating a branch in local:
Always create a new branch from the latest code of your base branch. So every time get the latest changes form remote repo and then create the new branch in local. Create the new branch from the base branch.
Check out to the base branch:
Other useful commands :
Check out to the base branch:
git checkout branchName
Get the latest code from remote:git fetch --al
git rebase origin/branchName
creating a new branch:git checkout -b branchName
(All the local changes you did on base branch will also exported to new branch that you create.)
list the local branches :
git branch
Delete an unwanted branch : (you cant do this when you are on the branch that you are trying to delete)git branch -D branchName
Handle with code related stuff
To see the local changes:
git status
To see what you have changed in a specific file :git diff /folder/filename.extension
use :q to come back
to force push any changes:git push --force origin branchName
Comments
Post a Comment